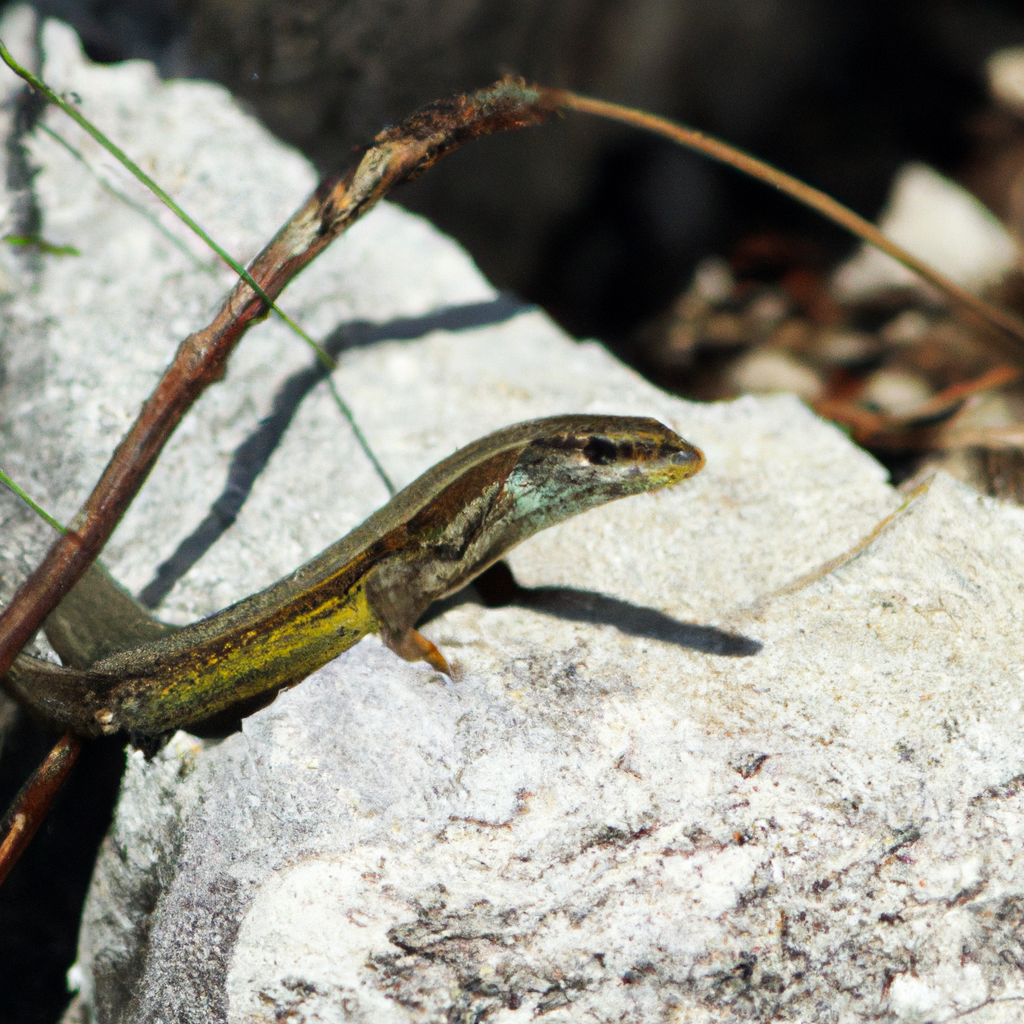
Introduction to Lizards in Europe
Lizards in Europe are a fascinating and diverse group of reptiles that inhabit various regions across the continent. From the Iberian Peninsula to the Balkans, Europe is home to a wide range of lizard species that have adapted to different environments and climates. These cold-blooded creatures play an essential role in the ecosystem, serving as both predator and prey in the food chain.
European lizards exhibit a wide array of colors, patterns, and sizes, making them intriguing subjects for nature enthusiasts and researchers alike. Some common species found in Europe include the Common Wall Lizard, European Green Lizard, and Viviparous Lizard. Each species has unique characteristics that help them thrive in their respective habitats.
One of the key factors contributing to the success of lizards in Europe is their ability to adapt to varying conditions. From rocky outcrops to sandy beaches, these reptiles can be found in a variety of landscapes, showcasing their remarkable resilience and survival skills. Furthermore, their behavior, such as basking in the sun to regulate body temperature or utilizing camouflage to avoid predators, adds to their allure and mystique.
Understanding the diversity and distribution of lizards in Europe is crucial for conservation efforts aimed at protecting these reptiles and their habitats. By studying their behavior, ecology, and population trends, researchers can develop strategies to ensure the long-term survival of these fascinating creatures. Overall, the study of lizards in Europe offers valuable insights into the interconnectedness of species and the importance of preserving biodiversity in the region.
Native Species of Lizards in Europe
Native Species of Lizards in Europe encompass a diverse range of reptiles that have adapted to various habitats across the continent. Some common species include the Common Wall Lizard, Sand Lizard, and European Green Lizard. These lizards exhibit unique characteristics that set them apart from each other, such as size, coloration, and preferred habitats.
The Common Wall Lizard, also known as Podarcis muralis, is a small lizard commonly found on walls and rocky outcrops in southern Europe. It is known for its ability to change color based on its surroundings, providing camouflage from predators. The Sand Lizard, or Lacerta agilis, is another native species that thrives in sandy habitats, such as dunes and heathlands. With its distinctive markings and agile movements, the Sand Lizard is a fascinating sight for nature enthusiasts.
The European Green Lizard (Lacerta viridis) is one of the largest lizard species in Europe, known for its bright green coloration and robust build. These lizards prefer sunny habitats with plenty of vegetation, where they can bask and hunt for prey. Their presence in certain regions indicates a healthy ecosystem, as they play a crucial role in controlling insect populations.
Overall, the native species of lizards in Europe contribute to the biodiversity of the continent and are essential components of their respective ecosystems. Understanding and appreciating these unique reptiles can lead to greater conservation efforts to protect their habitats and ensure their survival in the face of environmental challenges.
Habitats and Environments of European Lizards
In Europe, lizards can be found in a variety of habitats and environments, showcasing their adaptability to different ecological conditions. These reptiles are known to thrive in diverse settings, ranging from forests and grasslands to rocky outcrops and urban areas.
European lizards are often spotted basking in the sun on rocks or branches, making the most of the warm temperatures to regulate their body heat. They are also adept climbers, using their strong limbs and agile bodies to navigate through their surroundings with ease.
Some species of lizards in Europe are specialized for specific habitats, such as the sand lizard that prefers sandy heathlands or coastal dunes, while others like the common wall lizard can be found in a wide range of environments, including gardens and parks.
The diversity of habitats that European lizards occupy contributes to their ecological importance as key players in the local ecosystems. They serve as both predators and prey, helping to maintain the balance of their respective food chains.
Conservation efforts are essential to protect the habitats of European lizards and ensure their continued presence in the region. By understanding the specific habitat requirements of different lizard species, conservationists can implement targeted measures to safeguard these reptiles and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Overall, the habitats and environments of European lizards play a crucial role in their survival and well-being, highlighting the importance of preserving these diverse landscapes for the benefit of both lizards and the broader ecosystem.
Behavior and Characteristics of European Lizards
European lizards exhibit a wide range of behaviors and characteristics that make them fascinating creatures to study. These reptiles are known for their agility, quick movements, and unique adaptations that help them survive in diverse environments across the continent.
One common behavior among European lizards is basking in the sun to regulate their body temperature. They are ectothermic animals, meaning they rely on external sources of heat to maintain their body warmth. By basking on rocks or tree branches, lizards can absorb the sun’s rays and increase their energy levels for hunting and other activities.
European lizards also display various forms of communication through body language and vocalizations. Some species use head-bobbing, tail flicking, and color changes to signal aggression, courtship, or territorial boundaries. Understanding these behaviors can provide valuable insights into the social dynamics and interactions within lizard populations.
In terms of physical characteristics, European lizards come in a range of sizes, colors, and patterns. From the vibrant green hues of the emerald lizard to the camouflaged scales of the sand lizard, each species has evolved unique features to blend in with their surroundings and avoid predators. These adaptations demonstrate the remarkable diversity and evolutionary strategies that have allowed European lizards to thrive in their habitats.
Overall, studying the behavior and characteristics of European lizards not only offers a glimpse into their fascinating lives but also highlights the importance of conserving these reptiles and their ecosystems for future generations.
Conservation Status of Lizards in Europe
The conservation status of lizards in Europe is a topic of growing concern as habitat loss, climate change, and other human activities threaten their populations. Many species of lizards in Europe are facing challenges such as habitat destruction, pollution, and invasive species that are impacting their survival.
Efforts are being made to protect and conserve these reptiles in various European countries through conservation programs, research initiatives, and habitat restoration projects. Conservationists are working to raise awareness about the importance of preserving lizard populations and their habitats to maintain the balance of ecosystems.
One of the key aspects of conservation efforts for European lizards is to identify and protect critical habitats where these reptiles thrive. This includes creating protected areas, designating conservation zones, and implementing measures to reduce human disturbances in lizard habitats.
Conservationists are also conducting research to better understand the behavior, ecology, and population dynamics of different lizard species in Europe. This information is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies to ensure the long-term survival of these reptiles.
Overall, the conservation status of lizards in Europe highlights the need for collaborative efforts among researchers, conservation organizations, policymakers, and the general public to protect and conserve these fascinating creatures for future generations to enjoy.
Best Places to Spot Lizards in European Countries
When it comes to spotting lizards in European countries, there are several key locations that offer great opportunities for observation. From the sunny Mediterranean coasts to the lush forests of central Europe, the continent boasts diverse habitats that support a wide variety of lizard species.
One popular destination for lizard enthusiasts is the island of Crete in Greece, known for its warm climate and rich biodiversity. Here, you can encounter species like the Balkan Wall Lizard and the Snake-eyed Lizard in their natural habitats. Similarly, the rocky landscapes of southern Spain, particularly in regions like Andalusia, are home to iconic species such as the Iberian Wall Lizard and Ocellated Lizard.
For a unique experience, consider visiting the coastal areas of France, where you might spot the striking Blue Lizard or the Common Wall Lizard basking in the sun. The diverse ecosystems of Italy also offer fantastic opportunities for lizard sightings, with species like the Italian Wall Lizard and the Tyrrhenian Wall Lizard being common sights.
Eastern European countries such as Romania and Bulgaria are not to be overlooked, as they harbor species like the Green Lizard and the European Sand Lizard in their grasslands and woodlands. Whether you’re exploring the Mediterranean region or venturing into the continental heart of Europe, there are numerous locations waiting to be explored for a chance to observe these fascinating creatures in their natural environment.
Tips for Identifying European Lizard Species
When it comes to identifying European lizard species, there are several key features to look out for. One of the most distinguishing factors is the coloration and markings on the lizard’s body. Different species exhibit unique patterns and colors that can help in their identification. Paying attention to details such as the presence of stripes, spots, or other markings can be crucial in identifying the specific type of lizard.
Another important aspect to consider is the size and shape of the lizard. European lizards vary in size, from small and slender species to larger, more robust ones. Observing the body shape, tail length, and overall appearance can provide valuable clues in distinguishing between different species.
The head shape and features of European lizards can also be helpful in identification. Some species have distinct head shapes, crests, or markings that set them apart from others. Additionally, observing the eyes, nostrils, and mouth structures can aid in narrowing down the potential species.
Behavioral traits can also play a role in identifying European lizard species. Some lizards have specific behaviors such as basking in the sun, climbing trees, or burrowing in the ground. Understanding these habits and observing them in the wild can provide insights into the type of lizard you are encountering.
Overall, a combination of factors including coloration, size, shape, head features, and behavior can assist in accurately identifying European lizard species. Taking note of these characteristics and observing lizards in their natural habitats can enhance your knowledge and appreciation of these fascinating reptiles.
Interesting Facts About Lizards in Europe
European lizards are fascinating creatures with a variety of interesting facts that make them unique within the region. One intriguing aspect of these reptiles is their diverse coloration and patterns, which help them blend into their surroundings for camouflage and protection. Some European lizard species exhibit vibrant hues of green, brown, or even blue, making them a sight to behold in their natural habitats.
Another captivating fact about lizards in Europe is their ability to regenerate lost body parts. Many species of European lizards have the remarkable capability to regrow their tails if they are detached or injured, serving as a defense mechanism against predators. This regenerative ability sets them apart from other animals and showcases their resilience in the face of adversity.
Furthermore, European lizards are known for their unique feeding habits and diets. From insectivorous species that primarily consume insects to omnivorous lizards that also eat plants and small animals, these reptiles play an essential role in maintaining the ecological balance of their ecosystems. Their diverse dietary preferences contribute to the overall biodiversity of European habitats and showcase the adaptability of these fascinating creatures.
Overall, the interesting facts about lizards in Europe highlight the importance of these reptiles in the region’s ecosystems and the need to protect their habitats for future generations to appreciate and study. By understanding and appreciating the remarkable characteristics of European lizards, we can strive to conserve their populations and ensure their survival in the face of environmental challenges.
Importance of Lizards in European Ecosystems
Lizards play a crucial role in European ecosystems, contributing to the delicate balance of nature in various ways. As predators, lizards help control insect populations, including pests that can harm crops and vegetation. By feeding on insects such as beetles, grasshoppers, and spiders, lizards help maintain ecological harmony and prevent overpopulation of these smaller creatures.
Additionally, lizards serve as prey for larger predators, forming an essential part of the food chain in European habitats. Their presence supports the survival of species higher up on the food chain, such as birds of prey and mammals that rely on lizards as a food source. This interconnected web of relationships underscores the significance of lizards in sustaining biodiversity and the overall health of ecosystems in Europe.
Moreover, lizards contribute to seed dispersal through their foraging activities. Some lizard species consume fruits and seeds, subsequently dispersing these seeds across diverse habitats as they move around. This process aids in the regeneration of plant species and promotes the growth of vegetation in different areas, ultimately enhancing the biodiversity of European landscapes.
Overall, the presence of lizards in European ecosystems is vital for maintaining ecological balance, supporting biodiversity, and preserving the intricate relationships between species. Conservation efforts aimed at protecting lizard populations are essential not only for the survival of these fascinating reptiles but also for the overall health and sustainability of Europe’s natural environments.
Conclusion and Conservation Efforts for European Lizards
European lizards play a crucial role in their respective ecosystems, contributing to the balance and diversity of wildlife in the region. As key predators of insects and small invertebrates, lizards help regulate populations of these creatures, preventing overabundance and maintaining ecological harmony. By controlling insect populations, lizards indirectly benefit plants and crops, as unchecked insect populations can damage vegetation and crops.
Moreover, lizards serve as prey for various predators, forming an essential part of the food chain in European ecosystems. Their presence supports the survival and reproduction of higher-level predators, such as birds of prey and mammals, thereby enhancing overall biodiversity in the region. Without lizards as a food source, the populations of these predators could be negatively impacted.
In addition to their ecological importance, European lizards also serve as indicators of environmental health. Their presence or absence in specific habitats can reflect the overall well-being of ecosystems, as they are sensitive to changes in temperature, habitat loss, pollution, and other environmental factors. Monitoring lizard populations can provide valuable insights into the overall health of European ecosystems and help identify areas that may require conservation efforts.
Conservation initiatives aimed at protecting European lizards involve habitat preservation, restoration, and management, as well as efforts to reduce threats such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. By safeguarding the habitats of European lizards and promoting their conservation, we can help ensure the continued stability and resilience of European ecosystems for future generations.